uniaxial confined compression test hooke's law|hooke's law : services Can show that basis transformation rules for fourth-order tensors are analogous to tensors of any order (including vectors), i.e., given the representation of tensor C in two different bases ei , ̃ej : See more Caixa De Som Boombox Bluetooth Portátil 22cm Preto 110v/220v. O frete grátis está sujeito ao peso, preço e distância do envio. Frete grátis no dia Compre Bombomx .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB7 de dez. de 2023 · One of the most prominent platforms for her activism is the social media site X (formerly Twitter). Navratilova explains that her fervent engagement stems from her deep belief in freedom of speech .
Can show that basis transformation rules for fourth-order tensors are analogous to tensors of any order (including vectors), i.e., given the representation of tensor C in two different bases ei , ̃ej : See more
or just the plain equations exposing the actual couplings among normal and shear stresses and strains: See more ei )( ̃en Symmetries of the elasticity tensor How many different coefficients are there in a fourth order-tensor? . However, for the special case of the elasticity tensor, there are symmetries that reduce their number significantly. Implications of symmetry of stress tensor. This . See moreIf Hooke’s law (1) is applied for the elastic component and the associated °ow rule (8) for the plastic component, the complete stress-strain relationship for a material obeying a yield .
Uniaxial compressive strength is the maximum load carried by the speci-men divided by the cross-sectional area. The change in the specimen length is measured throughout the test, .
uniaxial strain test method
linear elasticity and hookes
Since the relationship between stress and strain must be uniform in order to determine the elastic constants, by applying the Hooke's Law, we must consider using a test device and a specimen configuration as well, to avoid perturbation .Hooke's Law describes linear material behavior. It is commonly used for isotropic materials (same behavior in all directions), but can also be extended to anisotropic materials. It is in fact .The simple relationship of uniaxial Hooke’s Law \(\sigma=E\varepsilon\) applies only in the case of uniaxial loading of a bar, since the lateral internal stresses \(\sigma_{22}\) and \(\sigma_{33}\) may not be zero for objects with greater .In Chapter 5, we discussed strain and the complexities of a material which could potentially have 21 independent elastic constants, and could be subjected to any stress state. Here, in considering the behaviour of real rock, we will begin with .
Uniaxial compression test (UCS) is one of the oldest and simplest rock mechanical test used to determine the Young’s modulus and unconfined compressive strength. It is also used as the most common simulation to .Hooke's law. Hooke's law is a law of physics which states that the force \(F \) needed to extend or compress a spring by an amount \(x \) scales linearly with respect to that amount, i.e. \begin{equation} F = .The boundary loading condition effect in concrete Uniaxial Compression Test (UCT) is studied to obtain the effect on the distribution of the strain and deformation fields by means of Digital .
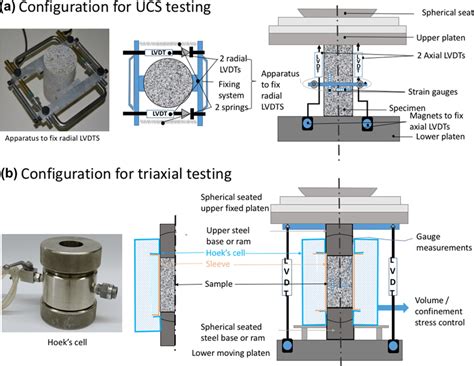
The uniaxial compressive strength (UCS) of rocks is a vital geomechanical parameter widely used for rock mass classification, stability analysis, and engineering design in rock engineering. Pressure-dependent yield: uniaxial strain and the layer compression test. It is interesting to note that the yield surface for some amorphous materials may increase under confined compressive stress faster than the generation of shear within the material, in principle precluding the system from ever reaching yield.
hooke's law 3 pdf
general Hooke’s law "ij = 1+” E 0 B B @¾ij ¡ ” 1+” –ij¾kk 1 C C A = C ¡1 ijkl¾kl; (1) where E is Young’s modulus, Cijkl the fourth-order stifiness moduli tensor and ” Poisson’s ratio. In a uniaxial tension or compression test, the only non-zero component ¾xx causes axial strain "xx and transverse strains "yy = "zz. Thus .The compressive strength of the material corresponds to the stress at the red point shown on the curve. In a compression test, there is a linear region where the material follows Hooke's law. Hence, for this region, =, where, this time, E refers to the Young's modulus for compression. In this region, the material deforms elastically and returns .
The two basic ways that compression testing can be implemented is by confined compression (Fig. 3 b) and unconfined compression (Fig. 3 a) (Griffin et al., 2016). In confined compression the sample is positioned inside an impermeable well and compressed with a porous platen, allowing fluid from inside the sample to be displaced vertically . The third major form for the stress strain model for concrete in compression uses an exponential function for the softening part of the curve (see Binici [23], Cusson [15], Hsu and Hsu [17], Shah et al. [24]).Binici [23] derived a stress strain relationship for the softening curve which assumes that the post-peak fracture energy per unit area under confinement is the .You may recall Hooke’s law from the study of the strength of materials, which states . . 129-mm-long rock specimen is subjected to a uniaxial compression test. The load–displacement plot is shown in Figure 3.4b. Determine the uniaxial strength and Young’s modulus of .Clearly, stress and strain are related. Stress and strain are related by a constitutive law, and we can determine their relationship experimentally by measuring how much stress is required to stretch a material.This measurement can be done using a tensile test. In the simplest case, the more you pull on an object, the more it deforms, and for small values of strain this relationship .
2003 yamaha yz125 compression test
This is the case of equibiaxial plane stress, meaning that the stress is confined to one plane (here, the 1–2 plane) and that the in-plane normal stress is independent of direction. . The simple relationship of uniaxial Hooke’s Law \(\sigma=E\varepsilon\) applies only in the case of uniaxial loading of a bar, since the lateral internal .In its simplest form, the uniaxial compression test is conducted by taking a right cylinder of intact rock, loading it along its axis and recording the displacement produced as the force is increased. In Figs 6.1 and 6.2 we present a typical record of such a test (which also includes the post-peak region obtained using techniques to be .Explanation: The unconfined compression test is a special case of tri axial compression test due to the absence of confining pressure, the uniaxial test is called the unconfined compression test. 3. The unconfined compression test is generally applicable to ____________ A uniaxial compression test was performed to evaluate the reinforcement effect of the preload generated by the high-temperature cooling of the tie rod on the core concrete. The results show that nylon ties can effectively improve the mechanical properties of the core concrete. . , and research on the damage evolution law of confined concrete .
With Uniaxial Compression Test (UCT) in practice, concrete specimens are not compressed in a pure uniaxial fashion. It is well-known that various influencing factors such as specimen or machine imperfections as well as the loading boundary conditions, specimen dimension, the location and length of extensometers, etc. will influence the response collected from the test.A typical stress-strain diagram deriving from a Uniaxial Compression Test of an undisturbed specimen of basalt is presented in Figure 1. The UCS is the peak value of the diagram and is equal to 44.7 MPa. Photos of the specimen before and after the test are presented in Figure 2. During the failure process, cracks propagated from the bottom to .compression test in redwood and then comparing them with uniaxial compression test. The current data may be considered to agree with the published values, except for the tangential directions.
The failure process is violent in the uniaxial compression test under axial strain control mode. In order to protect the extensometer from damage, only the uniaxial compression tests under lateral .2.7 Experiments. Experimental data of nine unfilled rubbers from quasi-static, uniaxial tensile tests as well as confined compression tests are employed, see Table 4, Fig. 1 and [].The uniaxial test data are used for the parameter identification of the \(\bar{I}_1\)-dependent strain energy functions \(W_{\textrm{iso},1}\) in Sect. 4.2, whereas the volumetric strain energy .
Consider a concrete specimen that is subjected to an external compressive evenly distributed applied pressure p c acting in the longitudinal direction (Fig. 3a), similarly to the specimen loaded in tension in Fig. 2.A uniform uniaxial state of stress, that is equal to the applied compression p c is developed. Corresponding axial compressive strains and lateral tensile . This is called Hooke’s law force, or spring force: \[F=-k x. \nonumber \] Here, \(F\) is the restoring force, \(x\) is the displacement from equilibrium or deformation, and \(k\) is a constant related to the difficulty in deforming the system. The minus sign indicates the restoring force is in the direction opposite to the displacement.Hooke’s Law is a fundamental principle in physics that describes the behavior of spring and elastic materials, particularly how they deform in response to an applied force. . In addition, Hooke’s Law is applicable only to uniaxial stress conditions, where the stress is applied in one direction and there is no stress in any other directions.Generalized Hooke's Law stress-strain calculator is used to calculate stress-strain relations of a homogeneous isotropic material under most general stress/strain conditions. If strains on a structure are measured in elastic range, stresses can be calculated from these results with the usage of Hooke's law strain - stress calculator.

I used to think that Hooke's law was a relationship between how much a bar under uniaxial loading deformed and the internal force (per unit area) that developed within that bar. But this clearly isn't the case as I have recently seen that Hooke's law is used in analyzing the stress in pure bending of beams. So it seems that Hooke's law is a lot more general than I had thought. where σ * is the normalized equivalent strength, σ ∗ = σ/f c, σ is the true stress, f c is the uniaxial compressive strength, and S max is the normalized maximum equivalent yield strength. P . If Hooke's law isn't specifically defined for a bar under uniaxial loading, what physical object is it exactly defined for? What system/object is Hooke's law trying to describe? My guess is that Hooke's law is defined for an infinitesimal cubic element which feels a normal stress on its sides from neighboring elements (picture below).
hooke's law
The uniaxial compression test is a destructive, time-consuming, and expensive test. Some of the research works that adopted uniaxial compression test to measure and estimate the mechanical . Hooke’s law in physics stated and explained with equations, diagrams, applications, and example problems. How are stress and strain applied to Hooke’s law. . This equation applies to both compression and extension of spring. The spring force can be measured using a spring tester or a weighing scale. The magnitude of the force is given by .
We have talked about Hooke's Law some already, and used it for tensor notation exercises and examples. . The first step in getting to the full model is to start with simple uniaxial tension/compression. In this case, the relationship is \[ \sigma = E \, \epsilon \] . is a material property just like \(E\) and requires a lab test to .
Mulher triste olhando para a câmera. 00:12. Menina chorando, de 1080 p. 00:15. Rosto de perto de uma jovem deprimida chorando e enxugando lágrima. 00:17. Triste pessoa .
uniaxial confined compression test hooke's law|hooke's law